- Doctors & Departments
-
Conditions & Advice
- Overview
- Conditions and Symptoms
- Symptom Checker
- Parent Resources
- The Connection Journey
- Calm A Crying Baby
- Sports Articles
- Dosage Tables
- Baby Guide
-
Your Visit
- Overview
- Prepare for Your Visit
- Your Overnight Stay
- Send a Cheer Card
- Family and Patient Resources
- Patient Cost Estimate
- Insurance and Financial Resources
- Online Bill Pay
- Medical Records
- Policies and Procedures
- We Ask Because We Care
Click to find the locations nearest youFind locations by region
See all locations -
Community
- Overview
- Addressing the Youth Mental Health Crisis
- Calendar of Events
- Child Health Advocacy
- Community Health
- Community Partners
- Corporate Relations
- Global Health
- Patient Advocacy
- Patient Stories
- Pediatric Affiliations
- Support Children’s Colorado
- Specialty Outreach Clinics
Your Support Matters
Upcoming Events
Mental Health Town Hall
Tuesday, April 23, 2024Join Children’s Hospital Colorado pediatric experts for a virtual...
-
Research & Innovation
- Overview
- Clinical Trials
- Q: Pediatric Health Advances
- Discoveries and Milestones
- Training and Internships
- Academic Affiliation
- Investigator Resources
- Funding Opportunities
- Center For Innovation
- Support Our Research
- Research Areas

It starts with a Q:
For the latest cutting-edge research, innovative collaborations and remarkable discoveries in child health, read stories from across all our areas of study in Q: Advances and Answers in Pediatric Health.


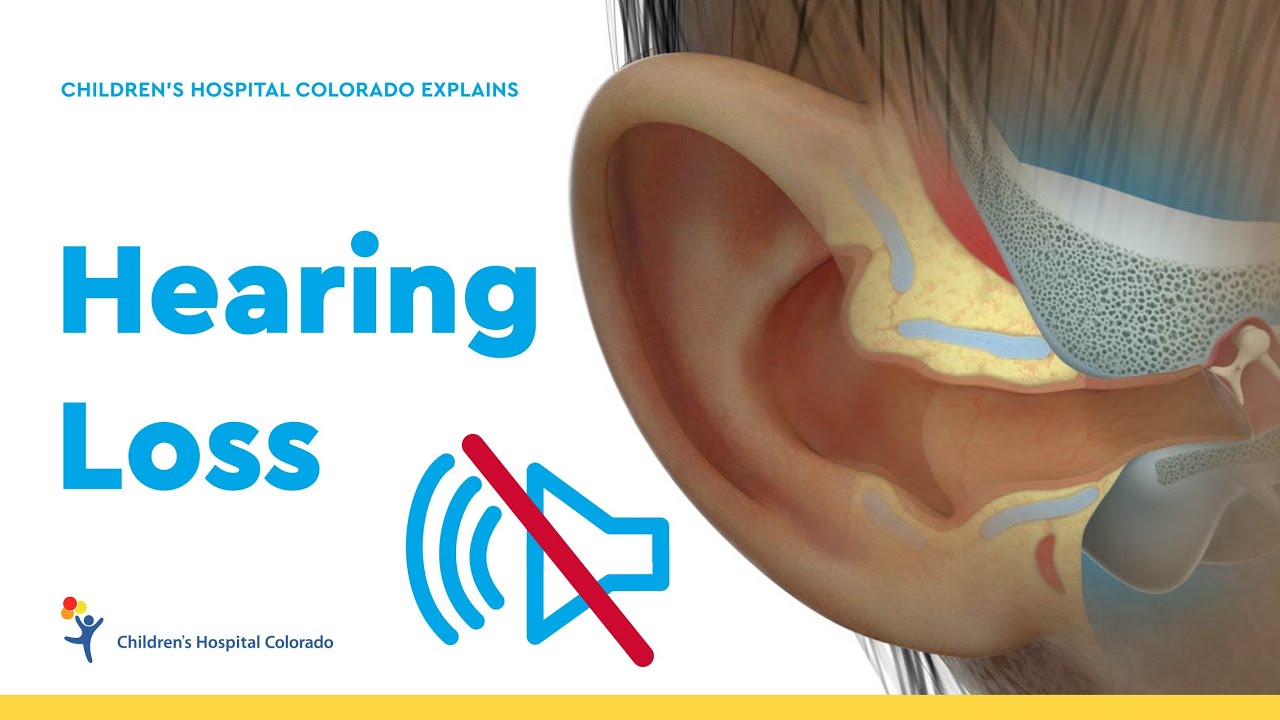
Ear, Nose and Throat
Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children
We see more, treat more and heal more kids than any other hospital in the region.

What is vestibular dysfunction?
Vestibular dysfunction is a vestibular disorder (a disorder relating to the inner ear and balance) that causes loss of balance and dizziness. The vestibular organs are located in the inner ears, next to the hearing organs. These organs sense movement in all directions and relay this information to the brain.
What is sensorineural hearing loss?
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL), or sensorineural deafness, is permanent hearing loss that can range from mild to total loss of hearing.
What causes vestibular dysfunction?
Vestibular dysfunction happens when there is damage to the vestibular system. We commonly see vestibular dysfunction in people with sensorineural hearing loss because the cause of their hearing loss may also cause damage to the vestibular organs. Vestibular dysfunction can also occur because of infection, head injury or exposure to certain medications that are ototoxic (toxic to the ear).
What causes sensorineural hearing loss?
Damage to the hearing organs in the inner ears, or to the nerves that attach the inner ears to the brain, can cause sensorineural hearing loss. Hearing loss can be the result of a congenital condition, meaning it’s present at birth, or it can be acquired by damage to the hair cells (small sensory receptor cells in the inner ear) or by damage to the auditory nerve.
Common causes of damage to the hearing hair cells that can lead to hearing loss include:
- Head injury
- Loud noises, such as an explosion or gunshot
- Exposure to ototoxic medications
- Medical conditions, either acquired or congenital
Some causes of permanent hearing loss are more likely to lead to vestibular dysfunction than others. Infections, disorders, tumors and treatments that can cause hearing loss and vestibular dysfunction include:
- Viral infections such as measles, meningitis, mumps and labyrinthitis
- Autoimmune disorders such as lupus and thyroiditis
- Tumors such as acoustic neuroma
- Congenital conditions such as cytomegalovirus (cCMV), enlarged vestibular aqueduct (EVA) and inner ear or 8th nerve malformations
- Genetic syndromes such as Usher’s, Waardenburg, Pendred, CHARGE and Alport
- Ototoxic medications including chemotherapy
- Cochlear implants
Who gets vestibular dysfunction?
Children with permanent hearing loss, including SNHL, commonly have balance problems — up to 70% of children with permanent hearing loss also have loss of vestibular function leading to balance problems. Children with higher levels of hearing loss are more likely to have vestibular problems.
What does the vestibular system do?
The vestibular organs are located inside the inner ears, next to the hearing organs. They sense movement and tell the brain where the person is in space. The central vestibular system in the brain gathers this information and tells the eyes and body to make changes to keep the person upright.
What are the signs and symptoms of vestibular dysfunction related to sensorineural hearing loss?
Your child’s symptoms may vary depending on whether they have vestibular dysfunction in one or both ears. It’s possible to have hearing loss in both ears but have vestibular dysfunction in only one ear. It’s also possible to have hearing loss in one ear but vestibular dysfunction in both ears. Some people may also have normal vestibular function in both ears despite having hearing loss in one or both ears. Because of these possible variations, vestibular testing with an audiologist (doctor of hearing and balance) is an important part of providing an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Possible symptoms include:
- Imbalance, clumsiness or frequent falls
- Increased imbalance or clumsiness on uneven surfaces or in low light environments
- Delayed movement milestones
- Difficulty reading
- Oscillopsia (objects appear to bounce)
- Nystagmus (irregular eye movement)
- Episodic vertigo (dizziness)
Vestibular testing helps us find out if there is anything abnormal with how your child’s inner ears sense movement, how they send that information to the brain and how the brain uses that information to maintain balance. Vestibular disorders related to hearing loss are diagnosed with a vestibular evaluation.
During a vestibular evaluation, your child will undergo a series of tests that target different parts of the vestibular system. Vestibular testing can begin as early as 6 months and your child can receive more tests when they turn 3 and again when they turn 7. Vestibular testing is based on age and developmental level and could include tests such as:
- Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials (VEMPs) – This test examines how sound might affect your child’s reactions.
- Video head impulse testing (vHIT) – This test tracks eye movement and fixed focus on a single point while your child’s head moves in different directions.
- Rotational chair testing – This test records how your child’s eyes move as their body rotates from left to right.
- Videonystagmography (VNG) or electronystagmography (ENG) testing – These tests track eye movement in different ways to see how your child’s eyes react to stimuli such as sound, lights and temperature.
- Oculomotor testing
- Headshake testing
- Positional/positioning testing
- Caloric testing
What can I expect from a vestibular test?
The first step is a vestibular evaluation, which may require a referral to our Audiology Department from your child’s doctor. This evaluation varies depending on your child’s age and developmental level and will be scheduled for either 1.5 hours or 2.5 hours.
Depending on the evaluation results, we may refer your child to our Pediatric Balance and Vestibular Disorders Clinic for a multidisciplinary exam by doctors from Otolaryngology (ENT), Audiology, Physical Therapy and Neurology. Sometimes we refer children directly to a vestibular physical therapist or neurologist without going through our Clinic.
How do we treat vestibular dysfunction related to hearing loss?
The most effective treatment for vestibular dysfunction related to hearing loss is vestibular physical therapy. This treatment can help with overall balance and dizziness symptoms. It can also help your child reach developmental milestones.
At Children’s Hospital Colorado, our vestibular audiologists work closely with our vestibular physical therapists to create a custom treatment plan based on the results from vestibular testing. The physical therapist will also check your child’s neurological, neuromuscular and musculoskeletal systems to make an individual care plan. Vestibular physical therapy is an effective way to help strengthen your child’s overall balance and help improve their quality of life.
Why choose us for treatment of vestibular dysfunction and sensorineural hearing loss?
The Pediatric Balance and Vestibular Disorders Clinic at Children’s Colorado specializes in caring for many vestibular disorders. When children complain of imbalance or dizziness, it could be the result of many different conditions. Our dedicated clinic helps diagnose and treat the full range of conditions related to these signs and symptoms.
Children’s Colorado is the only hospital in the state that has an enclosed rotary chair, necessary for assessing vestibular disorders in children with developmental differences. Without this testing, it’s difficult to completely rule out inner ear disorders in some children.
Helpful resources
The Vestibular Disorder Association (VeDA) provides education and emotional support for those with vestibular dysfunctions and advocate on behalf of all who are impacted by vestibular disorders.
Contacting us and making an appointment
Talk to your child’s doctor or managing audiologist about your concerns. We usually require a referral to both the audiology and physical therapy departments by a physician or advanced practice provider for vestibular testing and treatment.
We also want to ensure that the symptoms your child is experiencing do not require urgent medical attention. You can discuss these symptoms with one of our nurses who specialize in vestibular dysfunction and get advice by calling 720-777-8501.
We usually recommend vestibular testing to gather more information. If we recommend a vestibular evaluation, a scheduler will contact you to set up an appointment and provide additional instructions on how to prepare for the evaluation.
Next steps
-
Would you like to learn more about us?
Learn more about the Ear, Nose and Throat department -
Do you have questions about your child’s condition?
720-777-8501 -
Want a second opinion?
Get started



 720-777-0123
720-777-0123