- Doctors & Departments
-
Conditions & Advice
- Overview
- Conditions and Symptoms
- ¿Está enfermo su hijo?
- Parent Resources
- The Connection Journey
- Calma Un Bebé Que Llora
- Sports Articles
- Dosage Tables
- Baby Guide
-
Your Visit
- Overview
- Prepare for Your Visit
- Your Overnight Stay
- Send a Cheer Card
- Family and Patient Resources
- Patient Cost Estimate
- Insurance and Financial Resources
- Online Bill Pay
- Medical Records
- Política y procedimientos en el hospital
- Preguntamos Porque Nos Importa
-
Community
- Overview
- Addressing the Youth Mental Health Crisis
- Calendar of Events
- Child Health Advocacy
- Community Health
- Community Partners
- Corporate Relations
- Global Health
- Patient Advocacy
- Patient Stories
- Pediatric Affiliations
- Support Children’s Colorado
- Specialty Outreach Clinics
Your Support Matters
Upcoming Events
Mental Health Town Hall
martes, 23 de abril de 2024Join Children’s Hospital Colorado pediatric experts for a virtual...
-
Research & Innovation
- Overview
- Pediatric Clinical Trials
- Q: Pediatric Health Advances
- Discoveries and Milestones
- Training and Internships
- Academic Affiliation
- Investigator Resources
- Funding Opportunities
- Center For Innovation
- Support Our Research
- Research Areas

It starts with a Q:
For the latest cutting-edge research, innovative collaborations and remarkable discoveries in child health, read stories from across all our areas of study in Q: Advances and Answers in Pediatric Health.


Glossary of Terms Used in the Cleft Lip and Palate Clinic
We collaborate with every specialty in the hospital to advance new surgical techniques, teach tomorrow’s surgeons and give our patients a brighter today.
- Auditory brain response (ABR): a type of hearing test often performed after an infant fails the initial newborn hearing exam or when unable to complete a good hearing test; it is sometimes done under anesthesia
- Alar cartilage: cartilage that forms the outer side of each nostril
- Alveolus: the upper gum line; the part of the bony upper jaw that contains teeth
- Articulation: the formation of speech sounds
- Audiologic evaluation: a hearing test
 .
.
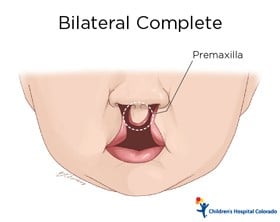
- Bilateral cleft: a cleft (split or opening) that occurs on both sides
- Bone morphogenic protein (BMP): a growth hormone that stimulates bone growth; it is used to fill in the gap in the gum line where the gum (alveolus) is clefted at the time of the bone graft surgery
- Cleft: a split or opening
- Columella: tissue at the base of the nose that separates the nostrils
- Congenital: existing at the time of birth
- Cross bite: when the upper teeth sit behind the lower teeth, instead of in front of them
- Deciduous teeth (baby teeth): a child’s first set of teeth; these teeth fall out as a part of normal development
- Denasality: vocal quality that lacks a normal nasal sound (sounds like a stuffy nose); also known as hypo-nasality
- Dental arch: the horseshoe shape of the upper gum
- Effusion: collection of fluid in the middle ear space; common among children with cleft palate and can negatively affect hearing
- Eustachian tube: the tube that connects the middle ear to the back of the throat
- Fistula: an abnormal opening that can occur after surgical repair of the palate
- Genetics: the science of genes and heredity
- Hyper-nasality: greater than normal nasal quality during speech
- Hypo-nasality: vocal quality that lacks normal nasal quality during speech (stuffy nose), (also known as denasality)
- Malocclusion: incorrect positioning of upper teeth in relation to lower teeth
- Mandible: the lower jaw, including the chin
- Maxilla: the bony upper jaw, including the area above the upper lip and under the nose
- Microform cleft: a very slight cleft (split or opening) in the lip or muscle of the lip
- Mixed dentition: period of time when children have both baby teeth and permanent teeth
- Nasal ala: wings or sides of the nostrils
- Nasal emission: amount of air that flows through the nose during speech
- Nasal regurgitation: food or liquids leaking out through the nose
- Nasal septum: internal structure that divides the nasal cavity
- Nasal endoscopy: a procedure in which a small camera is inserted through the nose to look at palate and throat movement during speech
- Nostril retainer: plastic device used after surgical repair of the lip and nose to help hold the shape of the nostrils as the tissue heals or to help keep the nostrils open
- Obturator: retainer-like device placed in the roof of the mouth to cover the cleft (split or opening); helps with feeding and speech development
- Occlusion: relationship between the upper and lower teeth when they are in contact
- Otitis media: ear infection

- Palate: roof of the mouth (made up of a hard section and a soft tissue section)
- Pharyngeal: relating to the pharynx or back of the throat
- Philtrum: middle of the upper lip

- Premaxilla: front central section of the upper gum usually containing the four upper front teeth
- Prolabium: front portion of the upper lip
- Resonance: quality of voice sound

- Submucous cleft: a cleft (split or opening) affecting the muscles that attach in the middle of the soft palate, but the visible skin is still intact
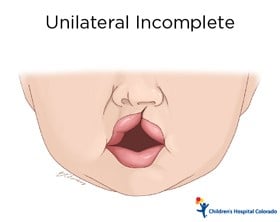
- Unilateral cleft: a split or opening (cleft) in one side of the lip or palate; can be completely open or partially slit
- Uvula: small cone-shaped tissue that hangs down from the soft palate in the back of the mouth; looks like a little punching bag
- Velopharyngeal closure: closure of the back end of the roof of the mouth (soft palate) and the back wall of the throat (pharynx)
- Velopharyngeal insufficiency (VPI): occurs during speech without a good seal between the nose and the mouth; resulting in hypernasal speech as air escapes from the back of the throat
- Vermillion: the vertical groove in the center portion of the upper lip
- Vermillion border: where the red portion of the lip meets the lighter skin portion of the lip



 720-777-0123
720-777-0123



