- Doctors & Departments
-
Conditions & Advice
- Overview
- Conditions and Symptoms
- Symptom Checker
- Parent Resources
- The Connection Journey
- Calm A Crying Baby
- Sports Articles
- Dosage Tables
- Baby Guide
-
Your Visit
- Overview
- Prepare for Your Visit
- Your Overnight Stay
- Send a Cheer Card
- Family and Patient Resources
- Patient Cost Estimate
- Insurance and Financial Resources
- Online Bill Pay
- Medical Records
- Policies and Procedures
- We Ask Because We Care
Click to find the locations nearest youFind locations by region
See all locations -
Community
- Overview
- Addressing the Youth Mental Health Crisis
- Calendar of Events
- Child Health Advocacy
- Community Health
- Community Partners
- Corporate Relations
- Global Health
- Patient Advocacy
- Patient Stories
- Pediatric Affiliations
- Support Children’s Colorado
- Specialty Outreach Clinics
Your Support Matters
Upcoming Events
Colorado Hospitals Substance Exposed Newborn Quality Improvement Collaborative CHoSEN Conference (Hybrid)
Monday, April 29, 2024The CHoSEN Collaborative is an effort to increase consistency in...
-
Research & Innovation
- Overview
- Pediatric Clinical Trials
- Q: Pediatric Health Advances
- Discoveries and Milestones
- Training and Internships
- Academic Affiliation
- Investigator Resources
- Funding Opportunities
- Center For Innovation
- Support Our Research
- Research Areas

It starts with a Q:
For the latest cutting-edge research, innovative collaborations and remarkable discoveries in child health, read stories from across all our areas of study in Q: Advances and Answers in Pediatric Health.


Gynecology
Ovarian Cysts
We specialize in the big things, the small things and everything in between.

What are ovarian cysts?
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs located within the ovaries. Many people develop ovarian cysts at some point, but most cysts are painless and harmless. In fact, a majority of ovarian cysts resolve themselves without treatment within a couple of months.
Some ovarian cysts can cause more serious symptoms and require treatment. For these more serious cysts, our care team at Children's Hospital Colorado will evaluate the cyst and work with a multidisciplinary team to develop the appropriate care plan.
What causes ovarian cysts?
Different cell types found in ovarian tissue cause different types of ovarian cysts. Many cysts develop as a result of the menstrual cycle, but less common cysts can develop in other ways.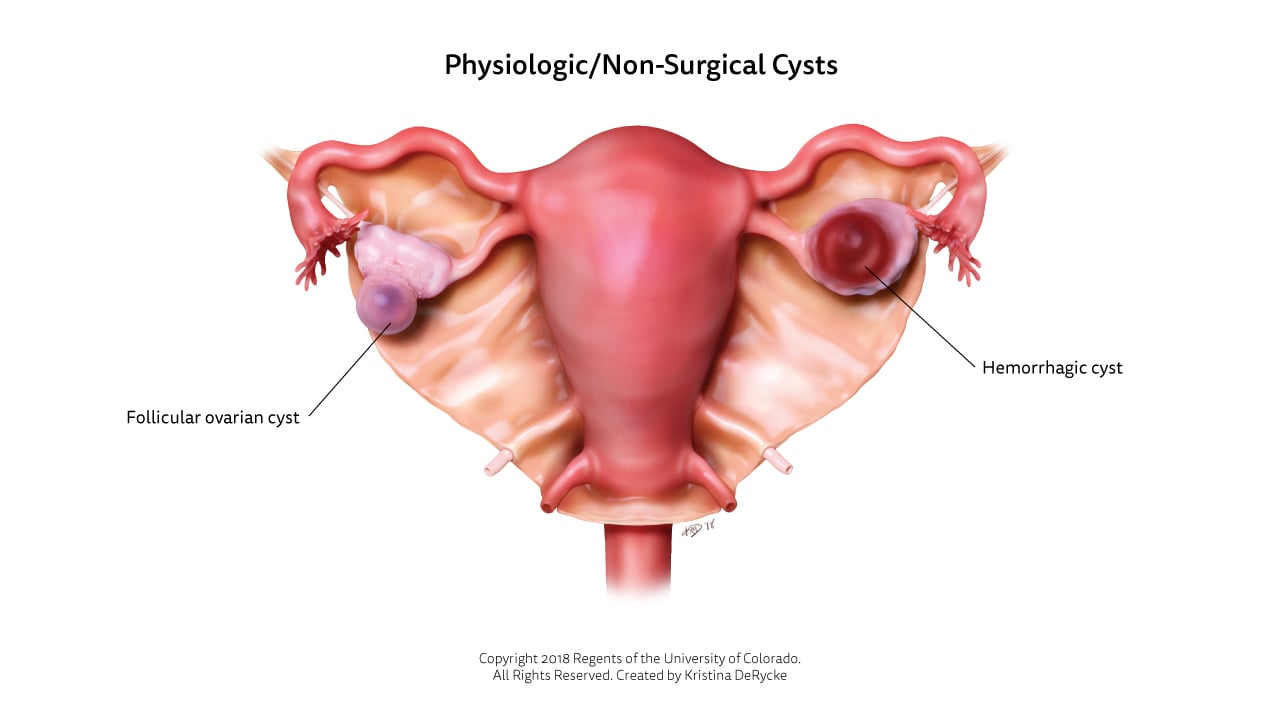
The most common type of ovarian cyst is called a "functional cyst" because it serves a purpose in the process of normal ovulation with each menstrual cycle. A single cyst will form around a maturing egg and grow to the size of a quarter just before it pops to release its egg into the fallopian tube. Occasionally, these cysts will grow larger and persist longer, but generally they resolve on their own within 6 to 8 weeks without treatment.
Usually, functional cysts are filled with clear fluid, but they can also contain blood. These cysts are referred to as "hemorrhagic corpus luteum" cysts and will also go away on their own. At times, some can develop ovarian cysts even before they start having menstrual cycles or when they are on medications to stop ovulation.
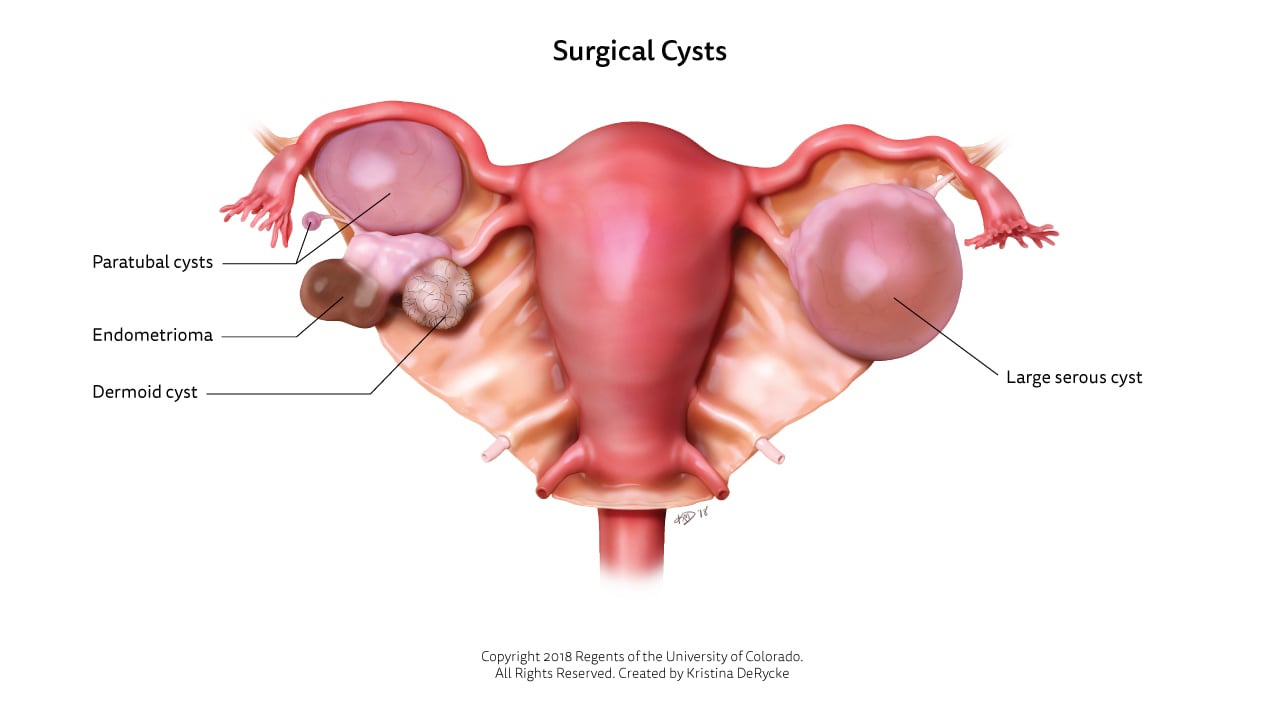
Other types of cysts occur when part of the ovary grows abnormally. These types of ovarian cysts will not go away on their own. They can arise from an overgrowth of cells on the surface of the ovary, the hormone-producing cells that surround an egg or the egg cell itself. In most cases, these types of cysts are benign (meaning non-cancerous) but some features may raise concerns about cancer, which requires careful care and treatment.
Who gets ovarian cysts?
All females of reproductive age will likely develop functional cysts at some point in their life. Ovarian cysts in teenagers are fairly common and typically don't cause further issues. The cyst may or may not be detected, depending on if it causes pain or if the patient receives a pelvic ultrasound or other imaging.
Nonfunctional cysts that occur because of a growth in the ovary are much less common. Ovarian cysts in general are more common in those who are pregnant or experiencing other issues, such as endometriosis, hormonal problems, severe pelvic infection or a previous ovarian cyst.
What are ovarian cyst symptoms?
Some ovarian cysts cause no symptoms and are incidentally found during imaging or testing done for other reasons. However, some experience:
- Acute pelvic pain, particularly when a cyst ruptures
- Pain between menstrual cycles that does not go away
- Bloating, pelvic pressure and back pain
Some other conditions can be mistaken for ovarian cysts, such as:
- Paratubal and urachal cysts
- Ovarian torsion
- Ovarian follicle
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
It is important that you talk with your gynecologist to understand what, if any, treatment or testing is needed for ovarian cyst pain or other symptoms you're experiencing.
Ovarian cyst tests and diagnosis
A pelvic ultrasound is the most common test to look for an ovarian cyst. Our care team uses a trans-abdominal (performed through the abdomen) or trans-vaginal (performed through the vagina) approach.
The trans-abdominal approach is much more common for girls and teens. It is important to have a full bladder before this test so we can view the ovaries completely.
For larger and more complicated cysts we may use magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or blood tests.
Repeated ultrasound testing is often necessary to confirm the resolution or persistence of the cyst.
Ovarian cyst treatment for adolescents
Treatment is different for each young person and may involve several approaches. Common ovarian cyst treatments for children and teens include:
- Monitoring through ultrasound
- Hormonal suppression
- Surgical evaluation
- Surgical removal
In many cases, we simply monitor smaller cysts that appear to contain fluid with repeated imaging to confirm the cyst has resolved or is shrinking. We may also recommend using hormonal therapy to prevent another functional cyst from forming in the future.
Persistent cysts with concerning characteristics may require surgical evaluation using a laparoscopic camera or a traditional abdominal incision.
We typically monitor a ruptured ovarian cyst with a repeat ultrasound in 2 to 3 months to ensure that it has resolved. Ruptured cysts often resolve themselves and we prescribe pain medication for comfort. Most of the time, we can manage ruptured ovarian cysts without surgery.
When surgery is required, our priority is to remove only the cyst and preserve any healthy ovarian tissue to preserve the eggs and ensure future fertility.
Why choose Children's Colorado for ovarian cyst treatment?
Accurate diagnosis and monitoring are necessary to properly treat ovarian cysts. Our adolescent gynecologists have extensive experience in evaluating children, teens and young adults with ovarian cysts and understand ovarian cyst causes that helps them easily explain test results. When needed, we work closely with our urology and pediatric surgery specialists to develop a management plan that maximizes future ovarian function and reproductive potential.
Because many of our younger patients are still developing, treating their ovarian cysts is different than treating cysts in adults. Our board-certified pediatric and adolescent gynecologists have specialized training in the reproductive health concerns of children and young people. We understand the complex changes that occur prior to and during puberty and can recognize both common and rare causes of ovarian cysts children and teens. We will put you or your child at ease by carefully explaining the medical condition and the options for treatment. We also support your family through follow-up and consultation with other specialists and your primary care doctor, as needed.
To learn more about ovarian cysts, visit:
Next steps
-
Would you like to learn more about us?
Learn more about the Gynecology department -
Are you ready to schedule an appointment?
Schedule an appointment -
Do you have questions about your child’s condition?
720-777-2667



 720-777-0123
720-777-0123







